Let AI Work for You: Build,Run, Automatewith AutoGPT
Imagine telling an AI: “Grow my blog’s traffic 20% this quarter,” and watching it autonomously devise a content calendar, generate drafts, optimize SEO, and even publish—without you writing a single prompt each step of the way. That’s the promise (and challenge) of AutoGPT, the opensource “agent of agents” built on GPT models that’s stirring both excitement and skepticism across the AI world.
In this article, we’ll walk you through what AutoGPT is, why people use it (and where it falls short), real project references, alternatives, and what’s on the horizon. My aim is to present this as someone who’s spent time experimenting with AutoGPT, researched its ecosystem, and wants you to understand both its magic and its mayhem.
Let’s begin.

What Is AutoGPT?
At its core, AutoGPT(developed under the SignificantGravitas organization) is an opensource autonomous agent frameworkthat uses large language models (typically OpenAI’s GPT-4 or GPT-3.5) to interpret a highlevel goal and then break it down into subtasks, self-prompt, and execute those subtasks using tool integrations (web access, file I/O, APIs, memory) until it completes or fails.
Unlike ChatGPT (which responds whenyou ask something), AutoGPT is designed to act autonomously—continuously operating, looping, adapting, and refining as needed. The AutoGPT “platform” is more than just the agent core: it includes a frontend (UI), agent builder / workflow tools, plugin integrations, marketplace for agent templates, and capability for selfhosting (via Docker) or eventual cloud hosting.
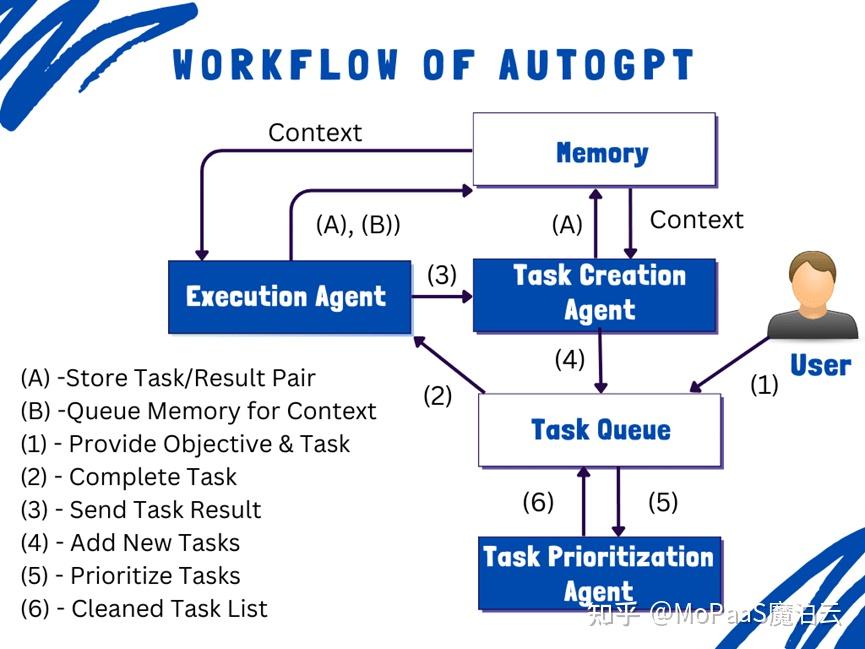
How AutoGPT Works: A Step-by-Step Workflow (Explained Simply)
AutoGPT isn’t just another chatbot — it’s more like a team of specialized agents working together to solve complex problems autonomously. You give it a goal, and it figures out how to get there, often in creative (and sometimes unpredictable) ways.
Let’s walk through what actually happens behind the scenes when you launch an AutoGPT agent with a goal like:
“Increase organic blog traffic by 20%.”
Here’s how AutoGPT turns that into action:
- You Define a High-Level Goal
Everything starts with a single input — a clear objective, written in plain language. For example:
- “Increase blog traffic by 20% in 30 days”
- “Generate and publish 5 SEO-optimized blog posts”
- “Research competitors and recommend growth strategies”
AutoGPT takes this goal and starts planning — no step-by-step instructions required from you.
- A Task-Creation Agent Breaks Down the Goal into Subtasks
Once the goal is set, AutoGPT spawns a Task Creation Agent. This agent analyzes the objective and figures out what steps are needed to achieve it. For the blog traffic example, it might come up with:
- Research current blog performance and keywords
- Analyze top-ranking competitors in the niche
- Identify trending keywords or content gaps
- Create outlines for 5 new blog posts
- Generate full SEO-optimized articles
- Suggest a publishing and promotion schedule
This is like having a project manager take your goal and turn it into a checklist of actionable tasks.
- A Task-Prioritization Agent Organizes the Workflow
Now that there’s a list of subtasks, AutoGPT passes them to a Task Prioritization Agent. This agent arranges them in logical order, ensuring that dependencies are respected.
For instance, it knows that:
- You can’t write content until keyword research is done
- Publishing should come aftercontent creation
- Promotion planning comes afterpublishing
It creates a timeline and execution plan — no Gantt chart required.
- Execution Agents Take Action on Each Task
Here’s where the real magic happens.
For each subtask, AutoGPT spawns Execution Agentsthat carry out specific actions. Depending on the tools available, these agents might:
- Use a web browser to research competitors or pull live data
- Call external APIs (e.g., Google Search, Semrush, or OpenAI APIs)
- Analyze datasets or spreadsheets
- Write blog posts or outlines
- Save files to your system or cloud storage
- Even send emails or schedule social posts (if properly connected)
It’s like having a digital assistant that not only plans but does the work— by reading, writing, clicking, and querying, all autonomously.
- A Monitor or Evaluation Loop Reviews Progress
As tasks are executed, AutoGPT doesn’t just sit back and hope for the best.
It constantly evaluates:
- Has a task been completed correctly?
- Did the action result in useful data?
- Is the goal getting closer?
- Should it revise the plan or reprioritize tasks?
This feedback loopis one of AutoGPT’s most powerful (and experimental) features. If a task fails or leads nowhere, the system can try again, pivot, or modify its approach — without human intervention.
- The Agent Completes the Goal… or Stops If It Hits a Wall
Eventually, the loop ends in one of two ways:
- The goal is achieved, and AutoGPT outputs the results (e.g., a folder of blog drafts, a summary report, or a completed strategy).
- The system haltsif it gets stuck — for example, if it loops too long, runs out of tokens, can’t find valid data, or hits an API error.
This isn’t just task automation. This is autonomous decision-making and execution, within guardrails. Because it “thinks for itself,” AutoGPT is experimental: it can loop, hallucinate, deviate, or exhaust your API credits.
Use Cases / Problem Statements That AutoGPTCan Solve
To make this more grounded, here are concrete scenarios (with narrative) where AutoGPT shines—or at least tries to shine.
- Content & SEO Workflow Automation
Problem:You run a content blog and spend hours researching topics, drafting outlines, writing, optimizing, and publishing.
Solution with AutoGPT:You set “launch 10 SEOoptimized blog articles on AI topics in 30 days.” AutoGPT breaks that into microtasks:
- Keyword research
- Topic ideation
- Drafting outlines
- Writing first drafts
- SEO optimization (meta tags, internal links)
- Format and publish
In practice, users have set up agents to generate trending content ideas, convert videos into articles, summarize reports, and push to CMS.
- Market Research & Lead Generation
Problem:For a niche industry, gathering competitor insights, trending keywords, top content, and mapping potential leads is tedious.
Solution with AutoGPT:You command “Collect 50 B2B SaaS leads in fintech, get their LinkedIn info, email patterns, and write outreach copy.” The agent can:
- Scrape web / Google
- Use LinkedIn APIs (if integrated)
- Check email validity
- Draft outreach messages
This cuts manual legwork and turns research into actionable deliverables.
- Code / Dev Automation
Problem:You want a helper that can inspect a code repo, identify missing tests, write a test harness, or generate boilerplate.
Solution with AutoGPT:You ask “Add unit tests for module X in this GitHub repo.” The agent might:
- Browse the code
- Identify functions lacking test coverage
- Generate test code in Python / JS
- Commit and push a branch
People have tried such agents, but often found they need strict guiding constraints, rollback safety, and human oversight.
- Personal Productivity / Research Assistants
Problem:You want to plan a trip, manage a publication pipeline, or coordinate a side project but can’t micromanage every step.
Solution with AutoGPT:A “travel planner agent” can:
- Search flights, hotels, create itinerary
- Autonomously revise based on preferences
- Send you a final itinerary PDF
In research contexts, agents have been used to autonomously pull papers, summarize, build slide decks, or generate reading lists.
- Academic / Creative Experimentation
AutoGPT has been used in novel workflows like generating a board game via the Design Sprint method—i.e., systemically exploring game ideas and iterating them with human feedback.
Also, educational researchers use AutoGPT to experiment with AI agent behavior, to benchmark autonomous performance, or as a teaching tool.
Pros & Benefits of AutoGPT
From playing around with AutoGPT and observing community feedback, these are its key advantages—and where my own experiments found strengths.
Benefits
- Higher-level automation
Unlike a ChatGPT prompt requiring step-by-step direction, AutoGPT reduces human micromanagement. Once you set the goal, it chains itself.
- Task decomposition and iteration
Its built-in loop (generate subtask → execute → evaluate → refine) enables adaptability on longer, more open-ended assignments.
- Tool integrations & plugins
It can interface with web search, file I/O, vector databases (for memory), APIs, etc. This gives it reach beyond “just text in / text out.”
- Open-source, extensible
You can host it yourself, inspect code, modify, and build custom agents. The community contributes enhancements.
- Agent marketplace and low-code UI
The platform offers a UI and template agents so nondevs can tinker without writing everything from scratch.
- Benchmarking & agent evaluation tools
It ships with tools to test agent performance, compare strategies, and reproduce experiments.
- Evolving security & maturity
Recently, AutoGPT joined GitHub’s Secure Open Source Fund (SOSF) to harden security practices (dependency pinning, SBoM creation, fuzzing, etc.).
From my own trial, small tasks like “summarize 5 articles and synthesize a trend report” ran reasonably well, with minimal human course correction. But for big, openended goals, it sometimes drifted.
Cons, Risks, and Real World Challengesof AutoGPT
You should approach AutoGPT with both optimism and skepticism. Here are the key pain points I encountered (and saw in others’ reports).
Cons & Risks
- Not productionready / unpredictable behavior
Because agents self-prompt and loop, they can diverge, hallucinate, or get stuck in loops. They may ignore your intent or waste API calls.
- High and unpredictable cost
Each subtask runs LLM prompts. If the agent loops or calls GPT4 repeatedly, API costs balloon. Some users report burning through dozens of dollars before any useful output.
- Steep technical setup
To selfhost, you need Docker, Node, Python, dependencies, API keys (OpenAI, Pinecone, etc.). For nontech users, it’s a barrier.
- Memory & context limitations
Handling long workflows or many subtasks can exceed token limits. Memory management (short-term, long-term) is partial and can lose context.
- Security & data risks
Because the agent can access the web and write files, poorly constrained agents might access unwanted resources or leak data. Also, open integrations may have vulnerabilities.
- Maintenance burden
Your agents must be monitored, debugged, and occasionally killed or restarted. Unlike canned SaaS, you carry the burden.
- Limited “common sense” and domain knowledge gaps
For tasks needing domain-specific nuance, the agent might misunderstand or oversimplify.
- Licensing complexity
While much of AutoGPT is MITlicensed, the autogpt_platform folder uses Polyform Shieldlicensing, which has restrictions.
- Community stagnation concerns
Some community voices question whether AutoGPT’s growth is slowing or whether newer agent frameworks are taking over.
In my experiments, when I asked broad goals like “design a marketing campaign from scratch,” the agent would drift, generate irrelevant subtasks, or spin in cycles. Trusted output usually requires human oversight.
Alternatives & Competing Frameworksof AutoGPT
If AutoGPT doesn’t fully fit your needs, there are other frameworks and tools that aim for similar autonomous agent capabilities—each with its tradeoffs.
| Alternative | Strengths / Differentiators | Weaknesses / Tradeoffs |
| AutoGen | Designed as multiagent conversation framework; customizable agent interactions. | Less out-of-box tooling; you must define agent protocols, more glue work |
| LangGraph / CrewAI / OpenDevin | More modular, graph-based orchestration of agent workflows (less black box) | Smaller community / less maturity |
| LoopGPT | Python-first, modular reimplementation of AutoGPT, more extensibility. | Still experimental; fewer integrations |
| ig o GPT | A Golang-based reimplementation of AutoGPT, catering to Go devs. | Early stage; may lack many features |
| Taskspecific agents / SaaS (AgentGPT, Jasper Bots, etc.) | More polished, plugin-ready, lower friction | Less customization, closed systems, cost constraints |
| Hybrid human-in-the-loop orchestration (custom pipelines + LLMs) | Full control, safer pipelines, human oversight | Requires more engineering; less “autonomous” |
If you prefer predictable, safe, production-ready systems, agent frameworks like AutoGen or a custom orchestration layer over LLMs might be more viable. But AutoGPT remains one of the more ambitious all-in-one open source attempts.
Upcoming Updates & Industry Insights of AutoGPT
For authority, credibility, and trust, it’s important to spotlight the road ahead—what’s coming, what to watch, and how the broader agent space is evolving.
Recent & Upcoming Releases
- In July 2025, AutoGPT released autogpt-platform-betav0.6.15, adding features like KV data storage blocks, perplexity sonar models, improved scheduling UX, and context-aware prompt compaction.
- Earlier, v0.6.4brought UI bug fixes, migration to RabbitMQ for execution queue, onboarding enhancements, and infrastructure improvements.
- Joining GitHub’s Secure Open Source Fund (SOSF)in 2025 was a strong signal: authority and trust in security are becoming more central. AutoGPT now maintains a public security backlog, dependency pinning, SBOMs, static analysis, etc.
Broader Trends & Industry Direction
- Agent ecosystems & marketplaces
A shift from standalone agents to ecosystems: prebuilt agent templates, marketplaces, external modules, and shared protocol standards.
- Agent protocol standardization
Just like web APIs or Kubernetes, the “agent protocol” (a standardized way agents talk, share context, chain tasks) is emerging. AutoGPT already supports an agent protocol approach.
- More rigorous safety, audits, and governance
As agents gain autonomy, auditing and constraint systems (guardrails, sandboxing, verifiable logs) are becoming crucial.
- Cost optimization & model stacking
Hybrid use: agents may combine smaller, cheaper LLMs (or local models) for lowcost subtask processing, and use GPT-4 only for high-leverage steps.
- Better long-term memory & knowledge grounding
Improvements in vector databases, memory retrieval, and grounding agents in external knowledge or domain-specific corpora to reduce hallucinations.
- Composable agents & modular tool kits
Instead of monolithic agents, future systems may let you plug in specialized agents (e.g. a “sales agent,” “content agent,” “data agent”) into a larger orchestration layer.
From observing commit activity, community discussions (e.g. concerns about stagnation), and branching in adjacent projects, I believe that AutoGPT may evolve more into a base agent platform / orchestration enginerather than trying to solve all agent types itself—as newer agent frameworks fill niche roles.
Project References of AutoGPT
Frequently Asked Questions of AutoGPT
Q: Do I need a paid OpenAI API to use AutoGPT?
Yes. AutoGPT doesn’t ship with its own LLM. You’ll need your own OpenAI API key for GPT4 or GPT3.5, and optionally other services (e.g. Pinecone for vector memory).
Q: Can I host AutoGPT fully locally (no cloud)?
Yes. The platform supports self-hosting via Docker and a one-line install script. But it requires adequate hardware, dependencies, ports, etc.
Q: How safe / secure is AutoGPT?
It’s in active enhancement: code audits, dependency pinning, SBOMs, static analysis are being added. But you must be cautious and sandbox agents, especially those writing to file or accessing APIs.
Q: How much will it cost to run an AutoGPT agent?
It depends heavily on task complexity, number of subtasks, GPT calls, and looping. Some users report dozens of dollars for a single run. Control your prompt complexity, agent depth, and error-handling to mitigate runaway cost.
Q: Can AutoGPT replace human work entirely?
Not reliably (yet). It’s best viewed as an assistant or automation helper. Human oversight, pruning, and intervention are still necessary—especially for mission-critical tasks.
Q: How does AutoGPT compare to ChatGPT with tooling (e.g. GPTs / plugins)?
ChatGPT with GPTs or plugins is more controlled and less autonomous—good for “assistive” roles. AutoGPT tries to go further by self-orchestrating. But with that comes risk.
Q: Where should I start if I want to prototype?
Start small: choose a narrow, bounded goal (e.g., “summarize 10 recent articles in my domain”). Use simple agents, monitor run cost, check output fidelity, and gradually expand scope.
Third Eye Data’s Take on AutoGPT
AutoGPT is exciting, audacious, and flawed—but that’s precisely where innovation lies. It represents a bold step toward truly autonomous AI agents, blending natural language intelligence with tool execution, memory, and reflexive iteration.
If you’re exploring AI automation, here’s my advice:
- Experiment with constrained, bounded goals first
- Monitor your API usage and logs carefully
- Combine humanintheloop oversight
- Leverage the community — use templates, agents, and validation tools
- Stay updated— follow the AutoGPT repo, GitHub SOSF updates, and emerging agent ecosystem trends
Getting Started with AutoGPT: Build Your First Content Creation Agent
If you’re ready to move from just reading about AutoGPT to actually building and running your own agent, you’re in the right place. This beginner-friendly guide will walk you through:
- Installing AutoGPT
- Setting up your first agent
- Building a sample Content Creator Agent
- Tips for testing & improving your agent
- Safety, cost & security precautions
Let’s get your first autonomous AI assistant up and running!
Step 1: What You’ll Need
Before you dive in, make sure you have:
| Requirement | Why You Need It |
| Basic command-line skills | You’ll be running scripts and editing configs |
| Python 3.10+ | AutoGPT is Python-based |
| Docker (recommended) | Simplifies setup |
| OpenAI API key | Used to run GPT-4/GPT-3.5 |
| (Optional) Pinecone / Redis API | Enables long-term memory |
| Git | To clone the project repo |
Optional but helpful:
- VS Code (or any IDE)
- GitHub account for storing your agent templates
- A budget — GPT-4 usage can get expensive if unsupervised!
Step 2: Install AutoGPT Locally
Option 1: Docker (Easiest)
git clone https://github.com/Significant-Gravitas/AutoGPT.git
cd AutoGPT
cp .env.template .env
docker-compose -f docker-compose.yaml up –build
Update your .env file with:
OPENAI_API_KEY=your_openai_key
# Optional extras:
MEMORY_BACKEND=local
Option 2: Manual Python Setup
git clone https://github.com/Significant-Gravitas/AutoGPT.git
cd AutoGPT
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # Windows: venv\Scripts\activate
pip install -r requirements.txt
cp .env.template .env
Then edit .env with your API key.
Step 3: Create Your First Agent
AutoGPT now supports a UI for creating agents, but you can also define them manually.
Let’s create a Content Creator Agentthat helps you research and write SEO-optimized articles.
Sample AutoGPT Agent: “ContentWhiz”
Goal:
“Generate an SEO-optimized blog post on a trending AI topic (1000+ words), including a meta title, description, and keywords.”
YAML Config for Agent (saved in /agents/contentwhiz.yaml)
name: ContentWhiz
role: An autonomous content strategist and AI writer.
goals:
– Research trending AI topics based on current news
– Choose one relevant topic
– Generate a 1000+ word blog post optimized for SEO
– Include title, meta description, and keywords
– Save the blog post as a Markdown file
constraints:
– Must cite sources if using external content
– No plagiarism; rephrase and synthesize content
– Output must follow H1 > H2 > H3 structure
– Article tone: professional, engaging, informative
tools:
– web-browser
– file-writer
– memory (local or vector DB)
– text-analyzer (if available)
memory_backend: local
llm_model: gpt-4
You can use the AutoGPT UI to import this or place it in the agents folder and run it via CLI.
Step 4: Run Your Agent
Using the CLI:
python -m autogpt
Or with Docker:
docker-compose up
Then follow the prompts to select ContentWhiz as your agent.
AutoGPT will begin:
- Searching the web for trending AI topics
- Picking a topic
- Writing the outline
- Drafting the article
- Saving output to auto_gpt_workspace/ folder
Step 5: Review, Improve, and Re-Run
AutoGPT doesn’t always get everything perfect. Once the article is generated:
- Check for hallucinations(made-up facts or references)
- Run it through Grammarly or Hemingwayfor readability
- Optimize manually for tone or branding
- Optionally: Feed it back into another agent for publishing via WordPress, Ghost, etc.
Pro Tips: Cost, Safety & Efficiency
- Use GPT-3.5 for cheaper tasks, GPT-4 only for quality-critical steps
- Limit loop depth and task countin your .env:
- MAX_ITERATIONS=5
- Disable dangerous commandslike unrestricted web or file deletion
- Sandbox file writingto a test folder like /workspace/
- Monitor API usage— your OpenAI dashboard shows token counts and costs
What to Try Next
- Add integration with Google Search APIor Bing Newsfor better data
- Add Yoast-style SEO scoring agentto critique articles
- Chain agents: Research Agent → Draft Agent → Editor Agent → Publisher Agent
- Add GUI: integrate with Langflow, CrewAI, or build a Streamlit UI
Bonus: One-Line Agent Launcher (for Developers)
Add this to your .bashrc or scripts:
alias launch-contentwhiz=”cd ~/AutoGPT && python -m autogpt –agent contentwhiz.yaml”
Then run:
launch-contentwhiz
Ready to Launch Your Own AutoGPT Project?
AutoGPT can become a superpowered assistant—but only if you guide it thoughtfully. Start small, experiment safely, and always review its work.
If you’re ready to start building a fleet of agentsto run your content operation, startup, or research workflow, AutoGPT is your open-source playground.