Amazon DynamoDB: The Engine That Delivers Millisecond Speed at Infinite Scale
The Relational Bottleneck: Why Traditional Databases Can’t Keep Up
In the era of microservices, global e-commerce, and real-time gaming, the demands placed on a database are simple: never slow down and never stop scaling.
If you’ve tried to meet this demand with a traditional relational database (RDBMS), you know the painful truth: they hit a hard limit. Manual sharding, complex replication, and constant server management crush developer agility and lead to inevitable downtime during critical traffic spikes.
This is the problem Amazon DynamoDB was engineered to solve.
DynamoDB is AWS’s fully managed NoSQL key-value and document database, based on the operational demands of Amazon.com itself. It’s not just fast; it’s designed for predictable performance, delivering single-digit millisecond latency at literally any scale—from a few requests per day to millions per second.
It’s serverless, globally resilient, and eliminates the most soul-crushing part of data architecture: infrastructure management. Simply put, if your application needs to be fast, reliable, and global, DynamoDB is the bedrock it must sit on.

Why DynamoDB is Your Strategic Advantage: Real-World Use Cases
DynamoDB wasn’t built for basic storage; it was built for operational warfare—handling unpredictable, high-volume traffic without blinking.
- The Real-Time Traffic Surge Warrior (E-commerce & Gaming)
- The Challenge: A flash sale, a viral marketing campaign, or a new game launch sends traffic spiking 10x in five minutes. Traditional databases crash or require massive, costly over-provisioning.
- The DynamoDB Fix: Using the On-Demand Capacity mode, DynamoDB auto-scales instantly to handle millions of reads/writes per second without a single change in configuration or a moment of downtime. It’s truly an elastic performance.
- IoT and Time-Series Ingestion
- The Challenge: Millions of devices generate high-volume, small, time-stamped events that need to be ingested quickly and automatically retired when stale.
- The DynamoDB Fix: Its high-write throughput is perfect for IoT sensor data. Furthermore, the Time-to-Live (TTL) feature automatically deletes expired records, making data lifecycle management effortless and cost-effective.
- Powering Serverless and Event-Driven Architectures
- The Challenge: Serverless functions (like AWS Lambda) have unpredictable spikes and require a database that can awaken and scale just as quickly.
- The DynamoDB Fix: As a serverless database, DynamoDB is the natural complement to Lambda. Its native integration with DynamoDB Streams enables real-time, event-driven processes, instantly feeding data changes into Kinesis, Lambda, or EventBridge.
- Enterprise-Grade Transactions and Compliance
- The Challenge: Many NoSQL databases sacrifice transactional integrity for speed, making them unsuitable for financial ledgers or high-stakes inventory management.
- The DynamoDB Fix: DynamoDB supports ACID Transactions, ensuring atomic, consistent, isolated, and durable operations across multiple items and tables. This makes it viable for fraud detection, payment processing, and core e-commerce logic.
- Global Applications with Zero Latency
- The Challenge: Serving users in London, Tokyo, and New York requires complex, cross-region replication that often suffers from latency and complicated conflict resolution.
- The DynamoDB Fix: Global Tables provides fully managed, multi-master replication across multiple AWS regions. Data written in one region is quickly available in others, delivering consistent, low-latency experiences to users worldwide.
The Technical Deep Dive: DynamoDB’s Core Strengths
| Key Feature | The Technical Advantage & Business Value |
| Fully Managed & Serverless | Zero Ops Burden. No patching, no backups, no cluster maintenance. Your developers focus 100% on application code and features. |
| Consistent Latency | Predictable User Experience. Guarantees single-digit millisecond response times, regardless of the scale—essential for real-time interactivity. |
| ACID Transactions | Enterprise Reliability. Supports atomic transactions, allowing it to reliably handle mission-critical financial and inventory workflows. |
| Flexible Schemas | Developer Velocity. As a document store, it allows different items in the same table to have flexible schemas, adapting easily as your business logic evolves. |
| Time-to-Live (TTL) | Automatic Cost Control. Automatically expires and deletes old data (like abandoned carts or stale logs), simplifying compliance and optimizing storage costs. |
| Security & Compliance | Trusted Infrastructure. Features include encryption at rest with AWS KMS, fine-grained access control via IAM, and full compliance with HIPAA and PCI DSS. |
The Consultant’s View: Overcoming the DynamoDB Challenge
While DynamoDB is an architectural powerhouse, it demands a different mindset than SQL. This is where the expertise of ThirdEye Data is crucial:
- Data Modeling is Everything
DynamoDB is optimized for access patterns, not relationships. A poorly designed partition key will lead to “hot partitions” (uneven data distribution) and costly throttling. Our focus at ThirdEye Data is on identifying your exact query patterns first to design composite keys and secondary indexes that guarantee consistent performance and minimal throughput consumption.
- Query Flexibility Limitations
DynamoDB excels at fast lookups via keys and indexes. It deliberately avoids complex, multi-table joins, and ad-hoc aggregations (like complex SQL).
- Our Solution: We architect the system to use Global and Local Secondary Indexes (GSIs/LSIs) for flexible lookups and use DynamoDB Streams with AWS Lambda to push data changes to a purpose-built analytics engine (like DynamoDB or S3/Athena) for complex reporting needs.
- Monitoring and Cost Optimization
While on-demand capacity is great for spikes, large, stable workloads often require tuning to Provisioned Capacity with Auto Scaling for better cost control. We implement detailed CloudWatch monitoring and cost alarms to ensure you are always in the most cost-effective capacity mode.
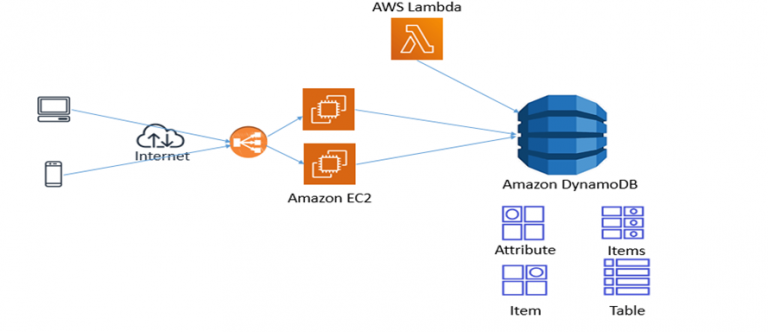
Amazon DynamoDB Flow Diagram
Image Courtesy: devopsschool.com
Frequently Asked Questions :
Q1: What type of database is DynamoDB?
DynamoDB is a NoSQL key-value and document database optimized for performance and scalability.
Q2: Can DynamoDB handle relational data?
While it’s not designed for relational joins, you can model relationships using composite keys and secondary indexes.
Q3: How does DynamoDB ensure data durability?
All data is replicated across three Availability Zones and stored on SSDs, ensuring 99.999% durability.
Q4: What is the difference between on-demand and provisioned capacity modes?
Provisioned mode: You define read/write capacity upfront.
On-demand mode: DynamoDB scales automatically based on traffic, ideal for variable workloads.
Q5: Does DynamoDB support transactions?
Yes. DynamoDB supports ACID-compliant transactions across multiple tables and items within a region.
Q6: Can DynamoDB integrate with AI/ML pipelines?
Absolutely. With DynamoDB Streams, you can feed real-time data into AWS Lambda or Amazon SageMaker for predictive analytics or AI workloads.
ThirdEye Data’s Strategic Recommendation
Amazon DynamoDB is the strategic choice for organizations pursuing data modernization, serverless architectures, and global application deployments. It is the database that was engineered for the scale and speed of the cloud.
If your ambition is to build applications that are infinitely scalable, globally distributed, and never compromised by infrastructure limitations, DynamoDB isn’t just an option—it’s the cornerstone of your architecture.
Partner with ThirdEye Data: Leverage our deep expertise in DynamoDB data modeling and optimization. We ensure your architecture harnesses its power correctly from day one, delivering reliable, millisecond performance and significant operational savings.
