React Native: Bridging the Gap Between Mobile Platforms and Performance
Introduction: One Codebase, a World of Possibilities
Imagine this.
You’ve just built a beautiful mobile app — sleek UI, smooth animations, feature-rich — but it’s only available for iOS. Now, your boss wants it on Android.
Traditionally, you’d have to start from scratch — new code, new language, new headaches. Twice the effort, twice the cost.
But what if there was a way to build both apps — iOS and Android — using one shared codebase, while keeping the performance and feel of native apps?
That’s the magic of React Native, a framework that has revolutionized mobile app development.

In the next few minutes, we’ll dive deep into:
- What React Native really is (and why it’s still a game-changer)
- How it connects the worlds of web and mobile
- The real-world use cases, pros, and cons
- Alternatives worth knowing
- And how top companies like Instagram and Tesla use it
By the end, you’ll not only understand why React Native continues to dominate mobile development — but also whether it’s the right choice for your next app.
What is React Native?
React Native is an open-source mobile application framework created by Meta (formerly Facebook). It allows developers to build cross-platform apps using JavaScript and React — the same principles that power modern web apps — and then render them using native components.
In simpler terms:
React Native lets you write once and run anywhere, producing truly native apps for both iOS and Android — without sacrificing performance.
At its core, React Native uses:
- React for component-based architecture
- JavaScript (or TypeScript) as the main programming language
- Native APIs to render UI components on both platforms
This means developers can leverage their existing web development skills to create production-grade mobile experiences.
A Brief History
React Native began as a hackathon project inside Facebook in 2013. The goal was clear: fix the inefficiency of maintaining separate iOS and Android codebases.
By 2015, Facebook open-sourced it — and the developer community embraced it with open arms.
Today, it’s used by tech giants including Instagram, Walmart, Shopify, Tesla, and Airbnb, powering apps used by hundreds of millions.
How React Native Works
React Native doesn’t use WebViews like older cross-platform tools.
Instead, it uses a “bridge” to communicate between JavaScript and native components.
Here’s how it works under the hood:
- The JavaScript code runs in a separate thread.
- It communicates via an asynchronous bridge to the native platform (Objective-C, Java, Kotlin, Swift).
- The app renders actual native UI components, not HTML.
This hybrid model gives the flexibility of JavaScript and the performance of native code, all while maintaining a single, unified codebase.
Use Cases / Problem Statements Solved with React Native
React Native isn’t just a developer’s convenience tool — it’s a business enabler.
Here’s where it truly shines.
1. Multi-Platform Mobile Development
Problem:
Companies often need to support both Android and iOS, but maintaining two separate teams doubles costs and slows releases.
Solution:
React Native lets teams share up to 90% of code across platforms.
That means one team, one codebase, and consistent UI/UX on both devices.
Example:
Shopify rebuilt several apps with React Native, reducing time-to-market by 50%.
2. Rapid Prototyping and MVP Development
Startups and product teams often need to validate ideas quickly.
React Native’s hot reloading, pre-built components, and shared logic make it ideal for building MVPs that can evolve into full-fledged products.
Example:
Startups can roll out MVPs to both stores in weeks instead of months, attracting investors faster.
3. Consistent UX Across Devices
React Native ensures visual consistency between iOS and Android without developers worrying about OS-specific quirks.
It uses Flexbox, similar to CSS, for layout — meaning designers can create responsive UIs that adapt perfectly across devices.
4. Integration with Existing Native Apps
React Native isn’t all or nothing. You can embed React Native components into an existing native app — a common strategy for companies transitioning to cross-platform.
Example:
Facebook originally integrated React Native into parts of its app before full adoption.
5. Real-Time and Data-Driven Applications
React Native supports real-time updates and dynamic data-driven UIs, making it ideal for:
- Chat applications
- News feeds
- E-commerce product pages
- IoT dashboards
With frameworks like Redux or MobX, managing global state becomes smooth and predictable.
6. Cost-Efficient Enterprise Apps
Enterprise environments often require multiple internal tools and dashboards. React Native lets organizations build these rapidly, while maintaining security and performance standards.
Example:
Walmart’s internal logistics apps run partially on React Native, unifying operations across departments.
Pros of Using React Native
Let’s explore why React Native continues to dominate the cross-platform space.
- Cross-Platform Development
Build for Android, iOS, and even web (via React Native Web) from one codebase. - Faster Development & Lower Costs
Shared codebase reduces development effort by up to 60%. - Hot Reloading for Instant Feedback
Developers can instantly preview UI changes without recompiling — saving hours during iteration. - Strong Community & Ecosystem
Thousands of libraries, plugins, and active contributors. You’ll never be short of solutions or support. - Near-Native Performance
React Native components map to actual native widgets — ensuring smooth animations and fast load times. - Easy Maintenance and Updates
Push updates simultaneously across both platforms with tools like CodePush. - Strong Backing from Meta and the Open Source Community
Continuous evolution ensures compatibility with the latest OS releases.
Cons / Limitations of React Native
Nothing is perfect — not even React Native.
Here’s where it faces challenges.
- Performance Overhead for Complex Animations
Apps with heavy 3D rendering or advanced animations may experience slight lag compared to pure native builds. - Native Module Dependency
You might still need native developers to bridge complex features like Bluetooth or ARKit. - Larger App Size
React Native apps can be heavier than their native counterparts due to additional layers. - Debugging Complexity
Bridging between JavaScript and native code sometimes causes debugging headaches. - Learning Curve for New Devs
Web developers need to understand mobile-specific concepts (navigation, permissions, lifecycle).
Alternatives to React Native
When choosing your mobile stack, it’s smart to explore the ecosystem.
1. Flutter (by Google)
- Uses Dart language.
- Compiles to native ARM code for faster performance.
- Great for UI-rich, animation-heavy apps.
- But has a smaller talent pool compared to React Native.
2. Swift (for iOS) & Kotlin (for Android)
- Full native experience with direct OS integration.
- Ideal for highly customized apps.
- But costly — requires separate teams and longer development cycles.
3. Xamarin (by Microsoft)
- Uses C# and .NET environment.
- Integrates well with enterprise infrastructure.
- However, slower community adoption.
4. Ionic / Capacitor
- Web-based hybrid apps using HTML, CSS, JS.
- Best suited for internal or low-complexity apps.
- Less performant than React Native or Flutter.
Each framework has its niche — but for scalability, speed, and cost-effectiveness, React Native often wins.
Upcoming Updates / Industry Insights of React Native
React Native continues to evolve rapidly — and 2025 promises exciting advancements.
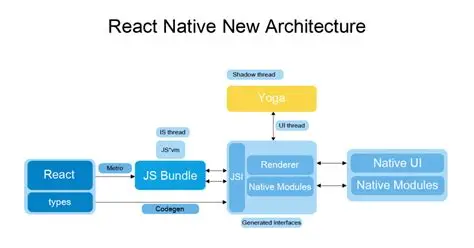
1. New Architecture (Fabric + TurboModules)
Facebook’s “New Architecture” overhaul improves rendering, startup times, and direct communication between JS and native threads.
2. Codegen and Type Safety
Improved TypeScript integration for better developer productivity.
3. Cross-Platform UI Consistency
Libraries like Reanimated 3, Gesture Handler, and Skia bring native-quality animations and GPU rendering.
4. Web and Desktop Expansion
Projects like React Native for Windows/macOS and React Native Web are extending its capabilities beyond mobile.
5. AI Integration in Tooling
AI-driven code assist tools (like GitHub Copilot or Meta’s own LLM-based assistants) are improving developer speed.
Industry Insight:
More enterprises are transitioning from hybrid to cross-platform development with frameworks like React Native — blending cost control with rapid innovation.
Project References
Frequently Asked Questions on React Native
Q1: Can React Native apps truly match native performance?
For most use cases — yes. Unless your app involves complex 3D graphics or VR, users won’t notice any difference.
Q2: Do I need separate developers for Android and iOS?
No. A single React Native team can build and maintain both.
Q3: Can I use native code with React Native?
Absolutely. You can write native modules in Swift, Objective-C, Java, or Kotlin and bridge them into your React Native project.
Q4: Is React Native good for enterprise applications?
Yes. Its scalability, reusability, and easy integration make it ideal for large-scale business applications.
Q5: How is React Native different from ReactJS?
ReactJS builds for browsers; React Native builds for mobile devices using native components instead of HTML tags.
Third Eye Data’s Take
The mobile ecosystem is evolving faster than ever — and businesses that move quickly win the market.
React Native stands out not just because it saves time and money — but because it empowers developers to build rich, performant, and visually stunning apps across platforms.
It bridges the best of both worlds — the flexibility of JavaScript and the performance of native.
Whether you’re a startup building your first app or an enterprise scaling to millions of users — React Native delivers consistency, speed, and excellence.
In a world that demands mobility and innovation, React Native isn’t just a framework.
It’s a movement— one that continues to redefine how we build digital experiences.
Call to Action: Build Once, Run Everywhere — Let’s Make It Real
Ready to take your mobile idea global?
With React Native, you don’t have to choose between performance, cost, or creativity.
Let’s build your next-generation mobile app — one codebase, two platforms, infinite impact.
[Contact Our Development Team] or [Schedule a Free Demo]