GCP’s Conversational Agents: Building Smarter Dialog with Google Cloud
The Conversational Revolution
Let me take you back a few years. You call a support center, navigate through a maze of “Press 1 for billing, Press 2 for technical” options, and finally speak to a human agent — if you’re lucky. It takes time, often frustration, and it’s costly for businesses.
Now imagine this: You open a chat on a website, ask a question like “My router is blinking red, how do I fix it?”, and get a helpful, context-aware answer — immediately. No waits, no confusion, and the conversation feels natural. That’s the promise of conversational agents— AI systems that understand human language and respond helpfully.
With Google Cloud pushing forward, GCP’s Conversational Agentsare evolving rapidly: powered by Dialogflow, Vertex AI Conversation, Agent Builder, and integrations with LLMs like Gemini. These tools help developers and organizations build robust chatbots, voice assistants, and conversational experiences that scale.
GCP Conversational Agents: Overview
“Conversational Agents” on Google Cloud refer to the suite of technologies and services that let you build chatbots, voice interfaces, virtual assistants, and dialog systems. These are powered by components like Dialogflow, Vertex AI Conversation / Agent Builder, and underlying NLP and generative AI models.
Key Capabilities
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU):Understand user intents, extract entities, parse user inputs.
- Dialog Management / Flows:Manage conversation state, transitions, fallback, and context.
- Generative Fallbacks / Hybrid Models:Use generative AI models when scripted responses don’t suffice.
- Multi-channel Deployment:Chat, voice, web widgets, phone integration.
- Integration with Enterprise Data & Tools:Connect to APIs, databases, knowledge bases, CRMs.
- Monitoring, Logging, Analytics, Security:Track conversation metrics, errors, user behavior, and ensure secure access.
Google’s Position & Strategy
Google’s conversational AI has evolved:
- Dialogflow (ES / CX):The longstanding Google conversational platform.
- Vertex AI / Agent Builder / Conversational Agents:Newer, more generative / hybrid systems integrating LLMs (Gemini, etc.), and deeper Google Cloud integration.
- Data Store Agent:A feature in Vertex AI Conversation that allows agents to ingest document sets, websites, or structured/unstructured data to power conversation.
- GenAI + Conversational Agents:Google is pushing generative fallback, modular “playbooks”, context routing, and better grounding.
In short: GCP’s Conversational Agents combine traditional NLP dialog toolswith modern generative AI and deep cloud integration.
Architecture & Connection: How Conversational Agents Are Built on GCP
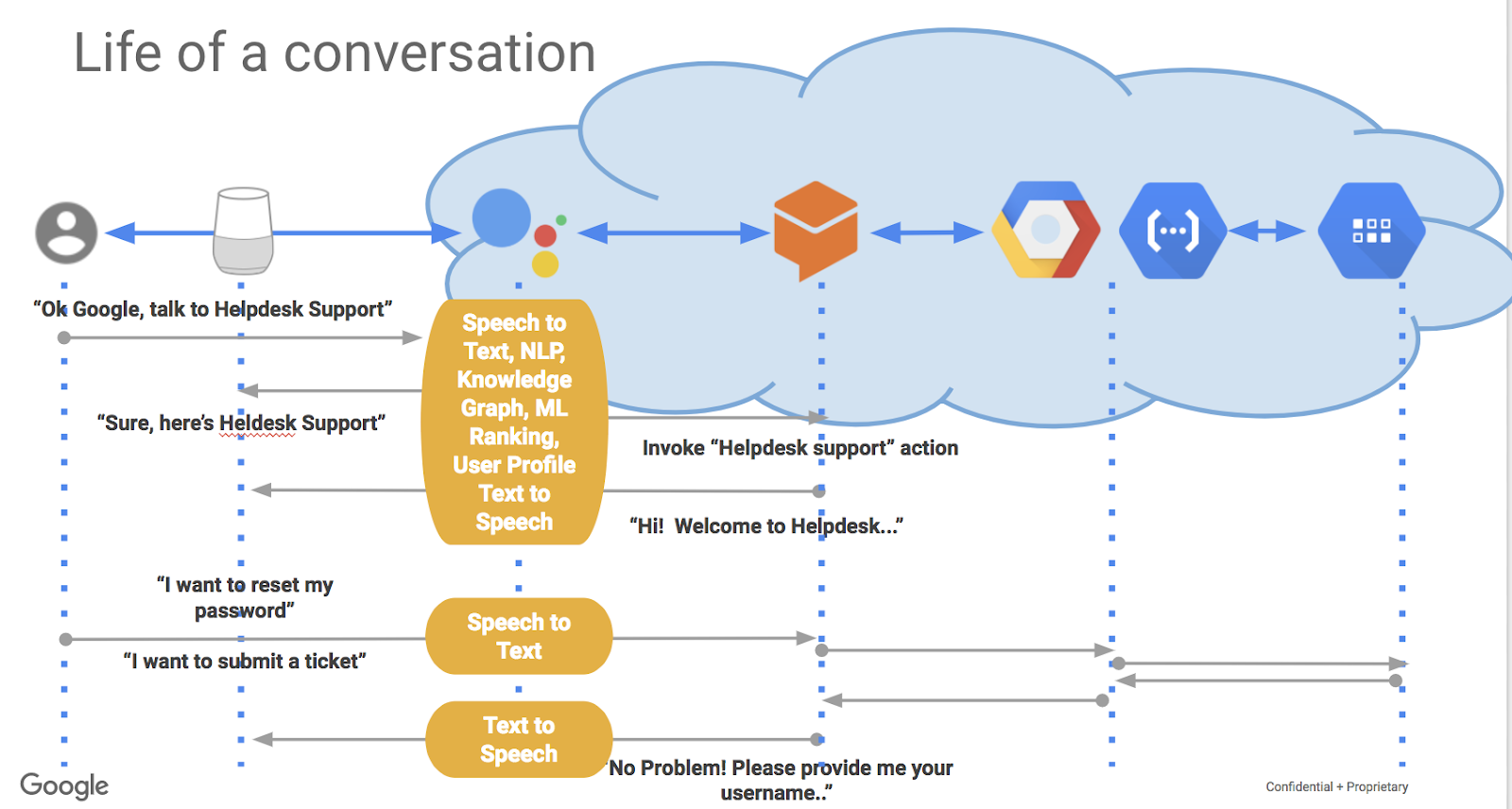
To understand the connection and how components work, let’s outline the architecture flow.
Core Components & Their Roles
| Component | Role / Function |
| Dialogflow CX / Agent / Conversational Agents UI | Core dialog design: intents, entities, flows, pages, transitions. |
| Data Store / Document Indexing | Agents ingest documents, structured/unstructured data to ground responses (Data Store Agent). |
| Generative Models / Fallback | When scripted responses don’t work, fallback to LLMs (Gemini, etc.) for generation. |
| Playbooks / Sub-Agents / Routing Logic | Agents route queries to sub-agents or playbooks based on intent, context. |
| Fulfillment / Webhooks / APIs | Agents connect to external systems — CRM, databases, transaction APIs — via webhooks or tool calls. |
| Channels & Frontends | Chat UI, voice, phone gateway, messaging platforms (web, Slack, Google Chat). |
| Monitoring / Analytics / Logging / IAM | Track conversation metrics, user satisfaction, errors, and control access. |
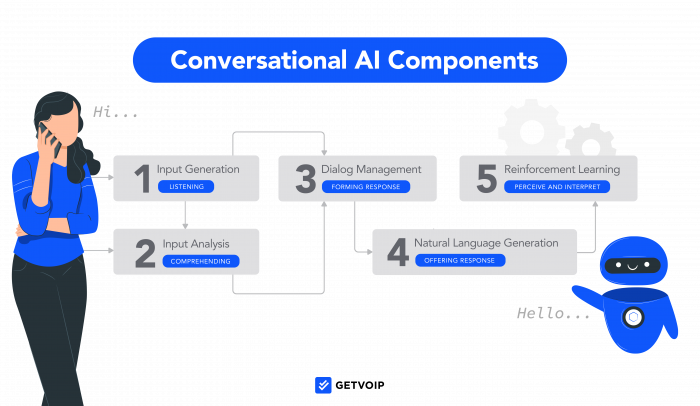
Conversation Flow (Step by Step)
- User Input
The user sends text or voice via web chat, phone, or app.
- NLU / Intent Detection
Dialogflow’s NLU engine analyzes the input, determines the intent, extracts entities, and maps to a flow or page.
- Routing / Context Resolution
Based on conversation state or playbooks, the agent decides whether to handle this in the current flow, switch to a subagent, or trigger generative fallback.
- Document / Data Lookup
If necessary, the agent queries the embedded knowledge base (via Data Store or index) to fetch context, facts, or relevant text.
- Response Generation
- Scripted Response:If the flow covers it, agent returns a designed response.
- Generative Response:If fallback, calls LLM with context and retrieved data to generate an answer.
- Fulfillment / Action Execution
Agent invokes webhooks or APIs to carry out tasks (e.g., “book a ticket,” “look up order number,” “update status”).
- Return Output
Agent responds with text, card, voice, or structured payload.
- Logging & Analytics
Conversation is logged, metrics captured (latency, success rate, fallback rate), and feedback used for improvements.
- Error / Fallback Handling
If the agent fails, fallback to error response or escalate to human agent.
Connection to Other GCP Services
- Vertex AI Search / Vector Retrieval
Conversational agents often integrate with Vertex AI Searchto retrieve relevant knowledge chunks before generating responses.
- BigQuery / Cloud Storage / Databases
Agents may query underlying data stores or export logs to BigQuery for deeper analytics.
- Cloud Functions / Cloud Run
Fulfillment logic often lives in serverless functions.
- IAM & Access Control
Use IAM to control who can build, view, or modify agents or access data.
- Logging / Monitoring / Observability
Integrate with Google Cloud Logging, Monitoring, and trace tools to monitor agent performance.
Use Cases / Problem Statements Solved by Conversational Agents
Let’s humanize this with real problems and how conversational agents address them.
- Customer Support & Contact Centers
Problem:Incoming customer tickets/calls overwhelm staff, many queries are repetitive.
Conversational Agent Solution:A virtual agent handles common issues (password reset, order status, troubleshooting), escalates to humans as needed, and learns over time.
Google’s Contact Center AI (CCAI), which uses conversational agents, is built for this.
- Internal Help Desks / Employee Assistants
Problem:Employees waste time searching policies, HR documents, IT guides.
Solution:An internal conversational agent able to understand corporate context, fetch relevant documentation, and guide workflows (e.g. “How do I claim travel reimbursement?”).
- Product & Website Conversational Interfaces
Problem:Users on websites are frustrated by poor site search or static FAQs.
Solution:Embed a chatbot widget that understands user language, points to relevant product pages or guides, helps navigation or bookings.
- Voice Interfaces & Smart Devices
Problem:Users expect natural voice interactions (phones, kiosks, assistants).
Solution:Conversational agents can support voice input/output, branching logic, and integrate with telephony systems via Dialogflow or Agent Builder.
- Knowledge-based Assistants & RAG Systems
Problem:LLM-based assistants hallucinate when they don’t know an answer.
Solution:Use conversational agents with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG)— agents fetch relevant documents or data and ground generative answers with them.
- Sales Assistants / E-commerce Support
Problem:Customers have queries about products, availability, specs, promotions.
Solution:Conversational agents help with product discovery (“Which laptop suits graphic design?”), order tracking, returns, recommendations.
Example Story
A mid-size telecom company had 10,000 customer calls daily for “service down,” “bill issues,” and “plan changes.” After deploying a conversational agent using Dialogflow + Agent Builder, they deflected 60%of repetitive queries, reduced average wait time, and allowed support staff to focus on complex issues.
Pros of GCP Conversational Agents
- Managed & Scalable
You get the power of Google’s infrastructure. Agents scale up under load with minimal setup. - Generative + Scripted Hybrid
The combination of structured flows and generative fallback ensures coverage for both well-known and novel queries. - Data Grounding & Citations
Because agents can fetch data from your knowledge store, responses can include source references, improving trust. - Multi-channel Deployment
Deploy across chat, voice, Google Chat, embedded widgets — seamless omnichannel experience. - Built-in Analytics & Monitoring
Track metrics like fallback rate, user satisfaction, conversation paths, and logs. - Tight GCP Integration
Easily circuit agents with BigQuery, Cloud Functions, GCS, IAM — fewer bolt-ons. - Low-code / Declarative Tools
Many parts (flows, example phrases, routing) can be configured declaratively, not from scratch coding.
Limitations & Challenges of GCP’s Conversational Agents
- Managed & Scalable
You get the power of Google’s infrastructure. Agents scale up under load with minimal setup. - Generative + Scripted Hybrid
The combination of structured flows and generative fallback ensures coverage for both well-known and novel queries. - Data Grounding & Citations
Because agents can fetch data from your knowledge store, responses can include source references, improving trust. - Multi-channel Deployment
Deploy across chat, voice, Google Chat, embedded widgets — seamless omnichannel experience. - Built-in Analytics & Monitoring
Track metrics like fallback rate, user satisfaction, conversation paths, and logs. - Tight GCP Integration
Easily circuit agents with BigQuery, Cloud Functions, GCS, IAM — fewer bolt-ons. - Low-code / Declarative Tools
Many parts (flows, example phrases, routing) can be configured declaratively, not from scratch coding.
Alternatives to GCP’s Conversational Agents
- Open-source frameworks:Rasa, Botpress, Chatbot frameworks allow full control at the cost of more infrastructure.
- Other cloud conversational platforms:Amazon Lex, Azure Bot Service, IBM Watson Assistant
- Custom LLM-powered solutions:Directly integrate LLMs (OpenAI, Anthropic) and build your own layering (retrieval, prompt engineering).
- Hybrid stacks:Use vector DB + prompt-based approach without full “agent” infrastructure.
These give trade-offs in control, cost, and maintenance
Upcoming Updates & Industry Trendson GCP’s Conversational Agents
- Stronger GenAI Integration
Google is pushing Generative fallback, steering agents, playbooks, and natural language instructionsfor building flows. - More Connectors & External Tools
Conversational Agents will likely support richer connections to APIs, enterprise systems, external “tools” or plugins. - Better Hybrid Search Retrieval
Tighter coupling with Vertex AI Searchor other knowledge retrieval systems for more accurate grounding. - Conversational Agents UI / Low-code Builders
Easier visual interfaces for non-developers to build or tweak conversations. - Agent Analytics & Automatic Improvement
Auto-identifying weak spots, suggesting improvements, A/B testing conversation flows. - Privacy, Compliance & Responsible AI
More controls for data privacy, audit trails, redaction, consent-based responses, etc.
Project References on GCP’s Conversational Agents
Frequently Asked Questions of GCP’s Conversational Agents
Q1: Are “Conversational Agents” just Dialogflow rebranded?
Not exactly. Dialogflow (CX / ES) is part of Google’s conversational stack. Conversational Agents / Agent Builder represent the next-gen, GenAI-enhanced evolution, integrating flows, playbooks, generative fallback, and deeper cloud integration.
Q2: Do I always need fallback to generative models?
No. Many queries are handled via structured flows and scripted responses. Generative fallback is used when no flow matches or to enrich responses.
Q3: Can conversational agents speak first (initiate conversation)?
Yes — by configuring the Start Page / Entry Fulfillmentin dialog flows. Some users report needing to enable “Entry Fulfillment” in start state.
Q4: How do I programmatically access conversational agents / API?
You can call Dialogflow CX APIs (SessionsClient, AgentsClient) or Google Cloud’s Agent/Conversation APIs. Some features are new or in preview.
Q5: Can I integrate external APIs / tools in an agent?
Yes. Agents can call webhooks, external services, and “tools” (via playbooks). Developers can enrich user queries with context before forwarding.
Q6: How do I test and iterate changes safely?
Use versioning, test flows and examples, simulation, and metrics to catch regressions.
Third eye Data’s Takeon GCP’s Conversational Agents
We’re in the age of conversational experiences— where users expect natural conversations, not rigid menus. With GCP’s Conversational Agents, you get a powerful blend of:
- Structured dialog systems(flows, intents, routing)
- Modern generative AI fallback
- Deep data grounding
- Scalability & enterprise integrations
- Analytics, security, and observability
Whether you’re building a customer-facing chatbot, an internal assistant, or an AI-enhanced website, these tools let you transcend old keyword-based bots. They enable agents that understand, reason, and serve— intelligently.
Call to Action:
Try the “Create a Generative Chat App” codelab today (Data Store Agent in Vertex AI Conversation). Build your first conversational agent over your own document set, test it, iterate, and see how natural language interactions elevate your user experience.