Welcome to the Amazon DynamoDB Developer Guide.
Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database service that provides fast and predictable performance with seamless scalability. DynamoDB lets you offload the administrative burdens of operating and scaling a distributed database so that you don’t have to worry about hardware provisioning, setup, and configuration, replication, software patching, or cluster scaling.
With DynamoDB, you can create database tables that can store and retrieve any amount of data, and serve any level of request traffic. You can scale up or scale down your tables’ throughput capacity without downtime or performance degradation, and use the AWS Management Console to monitor resource utilization and performance metrics.
DynamoDB allows you to delete expired items from tables automatically to help you reduce storage usage and the cost of storing data that is no longer relevant. For more information, seeTime To Live.
DynamoDB automatically spreads the data and traffic for your tables over a sufficient number of servers to handle your throughput and storage requirements, while maintaining consistent and fast performance. All of your data is stored on solid state disks (SSDs) and automatically replicated across multiple Availability Zones in an AWS region, providing built-in high availability and data durability.
We recommend that you begin by reading the following sections:
To get started quickly with DynamoDB, see Getting Started with DynamoDB.
To learn more about application development see the following:
To quickly find recommendations for maximizing performance and minimizing throughput costs see Best Practices for DynamoDB. To learn how to tag DynamoDB resources see Tagging for DynamoDB.
For best practices, how-to guides and tools, be sure to check the DynamoDB Developer Resources page: http://aws.amazon.com/dynamodb/developer-resources/.
You can use AWS Database Migration Service to migrate data from a Relational Database or MongoDB to an Amazon DynamoDB table. For more information, see AWS Database Migration Service User Guide. To learn how to use MongoDB as a migration source, see Using MongoDB as a Source for AWS Database Migration Service. To learn how to use DynamoDB as a migration target, see Using an Amazon DynamoDB Database as a Target for AWS Database Migration Service.
The following sections provide an overview of Amazon DynamoDB service components and how they interact.
After you read this introduction, try working through the Creating Tables and Loading Sample Data section, which walks you through the process of creating sample tables, uploading data, and performing some basic database operations.
For language-specific tutorials with sample code, see Getting Started with DynamoDB.
Topics
In DynamoDB, tables, items, and attributes are the core components that you work with. A table is a collection of items, and each item is a collection of attributes. DynamoDB uses primary keys to uniquely identify each item in a table and secondary indexes to provide more querying flexibility. You can use DynamoDB Streams to capture data modification events in DynamoDB tables.
There are limits in DynamoDB. For more information, see Limits in DynamoDB.
The following are the basic DynamoDB components:
The following diagram shows a table named People with some example items and attributes.

Note the following about the People table:
The following is another example table named Music that you could use to keep track of your music collection.

Note the following about the Music table:
When you create a table, in addition to the table name, you must specify the primary key of the table. The primary key uniquely identifies each item in the table, so that no two items can have the same key.
DynamoDB supports two different kinds of primary keys:
Note
The partition key of an item is also known as its hash attribute. The term hash attribute derives from the use of an internal hash function in DynamoDB that evenly distributes data items across partitions, based on their partition key values.
The sort key of an item is also known as its range attribute. The term range attribute derives from the way DynamoDB stores items with the same partition key physically close together, in sorted order by the sort key value.
Each primary key attribute must be a scalar (meaning that it can hold only a single value). The only data types allowed for primary key attributes are a string, number, or binary. There are no such restrictions for other, non-key attributes.
You can create one or more secondary indexes on a table. A secondary index lets you query the data in the table using an alternate key, in addition to queries against the primary key. DynamoDB doesn’t require that you use indexes, but they give your applications more flexibility when querying your data. After you create a secondary index on a table, you can read data from the index in much the same way as you do from the table.
DynamoDB supports two kinds of indexes:
You can define up to 5 global secondary indexes and 5 local secondary indexes per table.
In the example Music table shown previously, you can query data items by Artist (partition key) or by Artist and SongTitle (partition key and sort key). What if you also wanted to query the data by Genre and AlbumTitle? To do this, you could create an index on Genre and AlbumTitle, and then query the index in much the same way as you’d query the Music table.
The following diagram shows the example Music table, with a new index called GenreAlbumTitle. In the index, Genre is the partition key and AlbumTitle is the sort key.
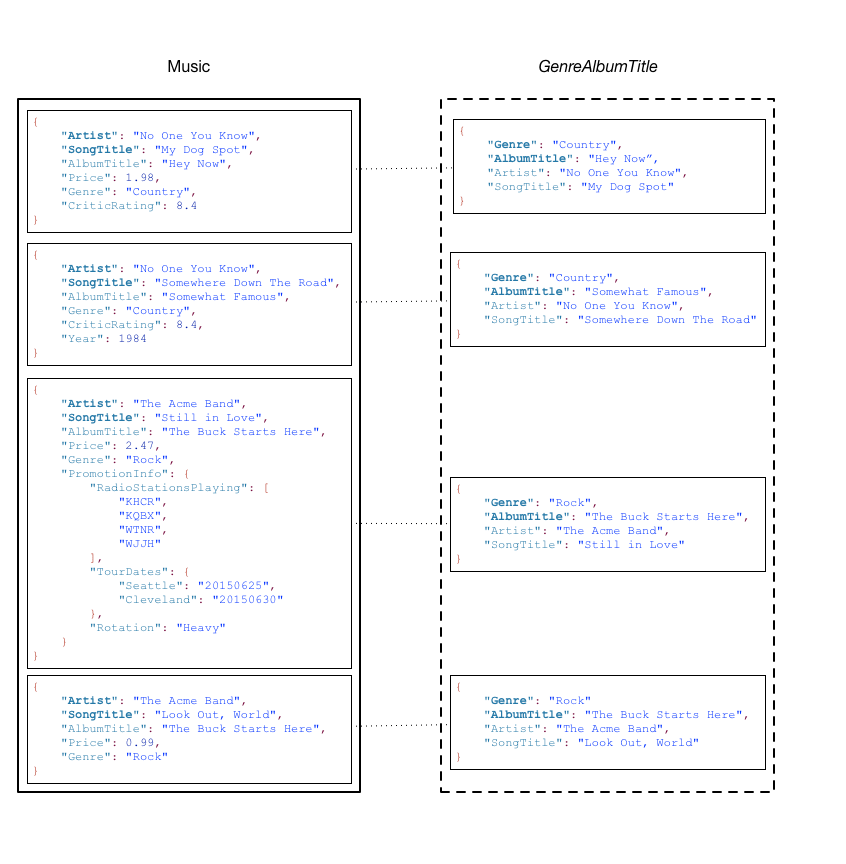
Note the following about the GenreAlbumTitle index:
GenreAlbumTitle where only the key attributes from the tableMusic are projected into the index.You can query the GenreAlbumTitle index to find all albums of a particular genre (for example, all Rock albums). You can also query the index to find all albums within a particular genre that have certain album titles (for example, all Country albums with titles that start with the letter H).
DynamoDB Streams is an optional feature that captures data modification events in DynamoDB tables. The data about these events appear in the stream in near real time, and in the order that the events occurred.
Each event is represented by a stream record. If you enable a stream on a table, DynamoDB Streams writes a stream record whenever one of the following events occurs:
Each stream record also contains the name of the table, the event timestamp, and other metadata. Stream records have a lifetime of 24 hours; after that, they are automatically removed from the stream.
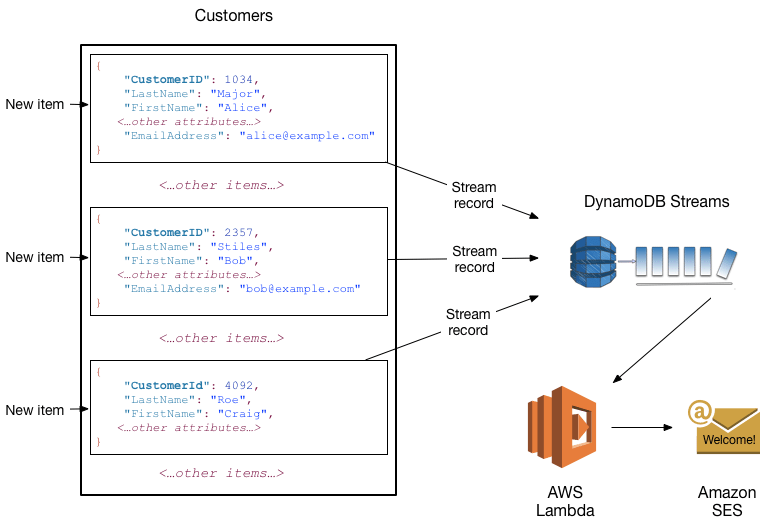
You can use DynamoDB Streams together with AWS Lambda to create a trigger—code that executes automatically whenever an event of interest appears in a stream. For example, consider a Customers table that contains customer information for a company. Suppose that you want to send a “welcome” email to each new customer. You could enable a stream on that table, and then associate the stream with a Lambda function. The Lambda function would execute whenever a new stream record appears, but only process new items added to the Customers table. For any item that has an EmailAddress attribute, the Lambda function would invoke Amazon Simple Email Service (Amazon SES) to send an email to that address.
Note
In this example, the last customer, Craig Roe, will not receive an email because he doesn’t have an EmailAddress.
In addition to triggers, DynamoDB Streams enables powerful solutions such as data replication within and across AWS regions, materialized views of data in DynamoDB tables, data analysis using Kinesis materialized views, and much more.
