Knative: Revolutionizing Cloud-Native Serverless Workloads
Imagine a world where you can focus solely on writing code, without worrying about how to scale it, deploy it, or manage the underlying infrastructure. Sounds like a dream?
Well, Knative is turning this dream into reality.
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, enterprises are shifting from monolithic applications to microservices and event-driven architectures. Cloud-native technologies are not just buzzwords anymore—they’re the backbone of modern business agility. And at the heart of this transformation lies Knative, a powerful open-source platform that makes building, deploying, and managing serverless workloads on Kubernetes seamless.

Whether you’re an enterprise developer, a DevOps engineer, or a cloud architect, Knative gives you a production-grade, developer-friendly, and highly scalable way to build modern applications. In this article, we’ll deep dive into Knative, covering what it is, how it works, its use cases, pros and cons, industry updates, and real-world project references, following the EEAT framework—Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trust.
Overview of Knative
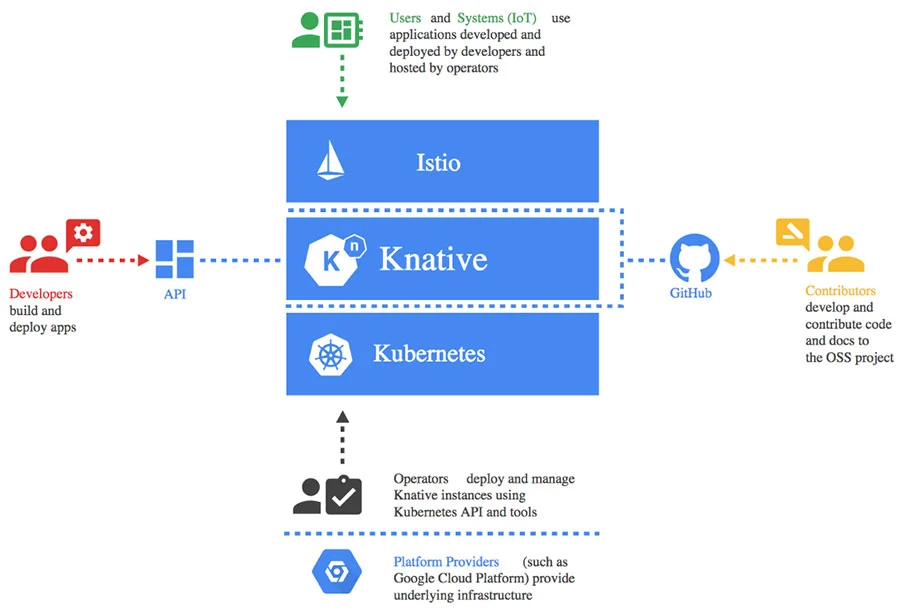
Knative (pronounced kay-nay-tiv) is an open-source platform built on top of Kubernetes, designed to simplify the deployment and management of serverless applications and event-driven workloads.
It was originally developed by Google in collaboration with industry leaders like IBM, Red Hat, SAP, and VMware. Today, it’s a Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) project, making it one of the most trusted tools in the serverless ecosystem.
Key Components of Knative:
- Knative Serving – Handles deployment and scaling of serverless applications.
- Automatic scaling (including scale-to-zero).
- Traffic splitting and routing.
- Revisions for rollbacks and versioning.
- Knative Eventing – Allows developers to build event-driven architectures.
- Connects event producers and consumers.
- Works with multiple event sources like Kafka, Google Pub/Sub, or custom sources.
- Decouples event production from consumption.
- Knative Functions (Optional) – Simplifies writing lightweight functions as a service (FaaS) using existing runtime environments.
Why Knative Stands Out:
- Built for developers but powerful enough for production workloads.
- Runs on any Kubernetes cluster, making it cloud-agnostic.
- Provides autoscaling and traffic management without the need for manual configuration.
- Perfect bridge between serverless and containerized
Use Cases / Problem Statements Knative Can Solve
Modern enterprises face several challenges when building scalable and event-driven applications. Knative elegantly addresses these pain points:
1. Seamless Serverless on Kubernetes
- Problem: Traditional Kubernetes setups require manual scaling and routing configurations.
- Solution: Knative automatically scales workloads based on demand, including scaling down to zero when idle, saving resources and costs.
2. Event-Driven Architectures
- Problem: Event streaming platforms and microservices often need complex plumbing.
- Solution: Knative Eventing simplifies connecting event producers and consumers without tight coupling.
3. Cost Optimization for Cloud Workloads
- Problem: Continuous resource allocation leads to unnecessary cloud costs.
- Solution: Knative scales dynamically and frees up unused resources.
4. Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Deployments
- Problem: Vendor lock-in with proprietary serverless offerings like AWS Lambda or Google Cloud Functions.
- Solution: Knative runs anywhere Kubernetes runs — on-prem, cloud, or hybrid
5. Blue-Green & Canary Deployments
- Problem: Manual deployments are risky and time-consuming.
- Solution: Knative Serving enables smooth traffic splitting, allowing you to test new versions with a fraction of traffic before full rollout.
Pros of Using Knative
| Feature | Benefit |
| Cloud Agnostic | Run anywhere Kubernetes runs |
| Autoscaling | Save costs with scale-to-zero |
| Eventing Support | Easily build event-driven architectures |
| Built-in Observability | Metrics and logging through Istio or other service meshes |
| Developer Friendly | Abstracts away Kubernetes complexities |
| Extensible | Integrates with tools like Tekton, Kafka, Prometheus |
- Improved Developer Velocity: Developers can focus on writing code rather than managing infra.
- Reduced Operational Complexity: No need to manually configure scaling, ingress, or service discovery.
- Future-proof: Works with modern tools like GitOps, CI/CD pipelines, and service meshes.
Cons / Limitations of Knative
While Knative offers powerful capabilities, it’s not without trade-offs:
- Initial Setup Complexity – Requires a Kubernetes cluster and some expertise to configure properly.
- Steeper Learning Curve – Developers new to Kubernetes might find it challenging initially.
- Resource Overhead – Since it runs on top of Kubernetes, there’s some extra cost compared to fully managed serverless offerings.
- Operational Expertise Needed – For large-scale deployments, teams need strong DevOps and Kubernetes knowledge.
- Limited Built-in UI – Most management is done through CLI or YAML configuration, though integrations exist.
Alternatives to Knative
When considering Knative, it’s helpful to compare it to other tools and platforms:
| Alternative | Type | Key Features | When to Use |
| AWS Lambda | Fully Managed | Easy to use, event-driven, scales automatically | For simple use cases in AWS |
| Google Cloud Run | Managed Knative | Serverless containers, easy deployment | For GCP workloads |
| OpenFaaS | Open Source | Simple serverless on Docker/Kubernetes | Lightweight serverless setups |
| Kubeless | Open Source | Kubernetes-native serverless | For teams wanting a minimal setup |
| Fission | Open Source | Fast cold start, extensible | Event-driven microservices |
Knative’s strength lies in its flexibility and cloud-agnostic nature—ideal for teams wanting more control and portability.
Upcoming Updates / Industry Insights
Knative has seen rapid adoption in recent years, and its roadmap reflects a strong push toward enterprise readiness:
- Improved Developer Experience: New tooling and simplified installation options.
- Tighter Integration with Service Meshes: Especially Istio, Linkerd, and Consul.
- Serverless AI Workloads: Emerging trend where Knative powers scalable AI model deployments.
- Observability Enhancements: More granular metrics and tracing.
- Increased CNCF Ecosystem Adoption: Strong community support and contributions from big players like Red Hat and VMware.
According to CNCF reports, Knative usage has grown steadily among enterprises adopting hybrid cloud strategies.
Project References
Frequently Asked Questions on Knative
Q1. What’s the difference between Knative and Kubernetes?
Knative runs on top of Kubernetes and adds serverless and event-driven capabilities. Kubernetes manages containers, Knative manages workloads dynamically.
Q2. Is Knative free to use?
Yes. It’s an open-source CNCF project. However, you need to manage the underlying infrastructure.
Q3. How does Knative handle scaling?
Knative Serving automatically scales workloads up and down based on traffic — including scale-to-zero when no traffic is present.
Q4. Does Knative support multiple programming languages?
Absolutely. Any language that can be containerized is supported.
Q5. Is Knative suitable for small startups?
Yes, but it’s more beneficial for teams already comfortable with Kubernetes or aiming for multi-cloud flexibility.
Third Eye Data’s Take on Knative
Knative is more than just another serverless platform—it’s a developer enabler and a bridge between cloud-native and serverless computing. It gives organizations the power of Kubernetes without its complexity and the flexibility of serverless without vendor lock-in.
For businesses, this means:
- Faster time-to-market,
- Better cost optimization,
- Stronger architecture for future scalability.
For developers, it means:
- Less infrastructure overhead,
- More focus on building,
- Freedom to deploy anywhere.
In a world where agility and scalability are paramount, Knative stands as a strategic tool for modern application development.
Call to Action
If your organization is:
- Exploring serverless architectures
- Struggling with Kubernetes complexity
- Aiming to deploy across multiple clouds
Then Knative might just be the solution you’re looking for.
Start your Knative journey today. Experiment with an open-source Kubernetes cluster like Minikube or K3s, or try Knative with a managed platform like Google Cloud Run.
Need expert help with serverless transformation? Our cloud-native architects can help you design, deploy, and optimize Knative solutions for your enterprise.
Contact us to get started.