Apache Tez: Explanation, Guide & Insights by ThirdEye Data
What Is Apache Tez? Efficient Data Processing on Hadoop Explained
The Apache TEZ® project is aimed at building an application framework which allows for a complex directed-acyclic-graph of tasks for processing data. It is currently built atop Apache Hadoop YARN.
The 2 main design themes for Tez are:
- Empowering end users by:
- Expressive dataflow definition APIs
- Flexible Input-Processor-Output runtime model
- Data type agnostic
- Simplifying deployment
- Execution Performance
- Performance gains over Map Reduce
- Optimal resource management
- Plan reconfiguration at runtime
- Dynamic physical data flow decisions
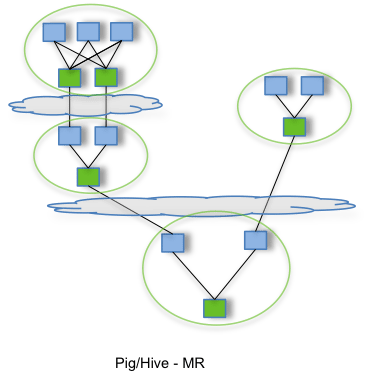
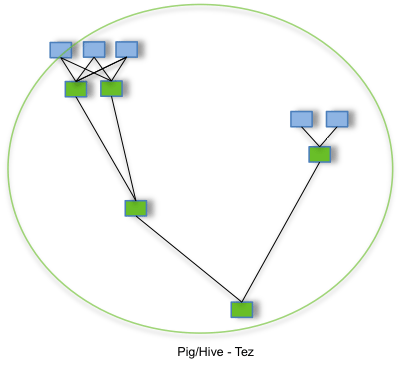
By allowing projects like Apache Hive and Apache Pig to run a complex DAG of tasks, Tez can be used to process data, that earlier took multiple MR jobs, now in a single Tez job as shown below.
Tez Local Mode
Tez Local Mode is a development tool to test Tez jobs without needing to bring up a Hadoop cluster. Local Mode runs the Tez components AppMaster, TaskRunner that are used when executing a job on a cluster. From a developer tool perspective, it offers several advantages.
- Fast prototyping Hadoop setup, launch cost etc not involved.
- Unit testing Fast execution since the overhead of allocating resources, launching JVMs etc is removed.
- Easy debuggability Single JVM running all user code.
While majority of the components are reused in Local Mode, there are some bits which are not
- Scheduling and Container Re-Use differs.
- Handling of YARN Local Resources. Local Mode expects necessary jars to be loaded with the Client when executing.
- Contains some performance improvements like skipping RPC invocations since everything runs within the same JVM.Running a DAG in Local Mode
- “tez.local.mode” should be set to true in the confgiuration instance used to create the TezClient.
- The FileSystem must be configured to the local file system (“fs.default.name” must be set to “file:///”). This is required to be setup in all Configuration instances used to create a DAG. Typically, when using Tez for testing and prototyping without a Hadoop cluster, this is not a problem. It becomes a problem when Hadoop Configuration files are in the classpath, with a different default filesystem configured.
- Setup the fetchers to make use of local reads instead of fetching from remote nodes. (“tez.runtime.optimize.local.fetch” must be set to true)
- Beyond this, no other changes are required, to make use of Local Mode instead of running a job on a cluster.
- If using this in code, the following changes should be made to configuration, after which this configuration instance becomes the base for all other Configuration instances.
Configuration conf = new Configuration(); conf.setBoolean(TezConfiguration.TEZ_LOCAL_MODE, true); conf.set("fs.default.name", "file:///"); conf.setBoolean(TezRuntimeConfiguration.TEZ_RUNTIME_OPTIMIZE_LOCAL_FETCH, true); - If using a tez-site.xml config file, it should contain the following entries
fs.default.name file:/// tez.local.mode true tez.runtime.optimize.local.fetch true
Things to watch out for
- In current Local Mode, large amount of input data may lead to JVM out of memory since all TEZ components are running in single JVM. The input data size should be kept small.
- TezConfiguration.TEZ_AM_INLINE_TASK_EXECUTION_MAX_TASKS(tez.am.inline.task.execution.maxtasks) should not be changed (defaults to 1).
- “tez.history.logging.service.class” should be the default value: “org.apache.tez.dag.history.logging.impl.SimpleHistoryLoggingService”. It means ATS is disabled in current Local Mode.
Potential pitfalls when moving from Local Mode to a real cluster
- Resource requirements (CPU, Memory, etc) which would otherwise have been specified for a YARN Cluster will now start taking affect, and should be considered.
- The Java Options and Environment variables which may have been setup for the DAG do not take affect in Local Mode, and could be a source of migration problems.
- The ObjectRegistry will work within a single task, when running in Local Mode. The behaviour would be different on a real cluster, where it would work across tasks which share the same container.
Local Mode with External Services
- When running in local mode, regular container execution is converted to run within the same process, instead of launching containers.
- Execution that is configured to run in external services is unaffected, and an attempt is made to make use of these external services for execution. If configured in this manner, make sure that the external services are running when attempting to use local mode.


